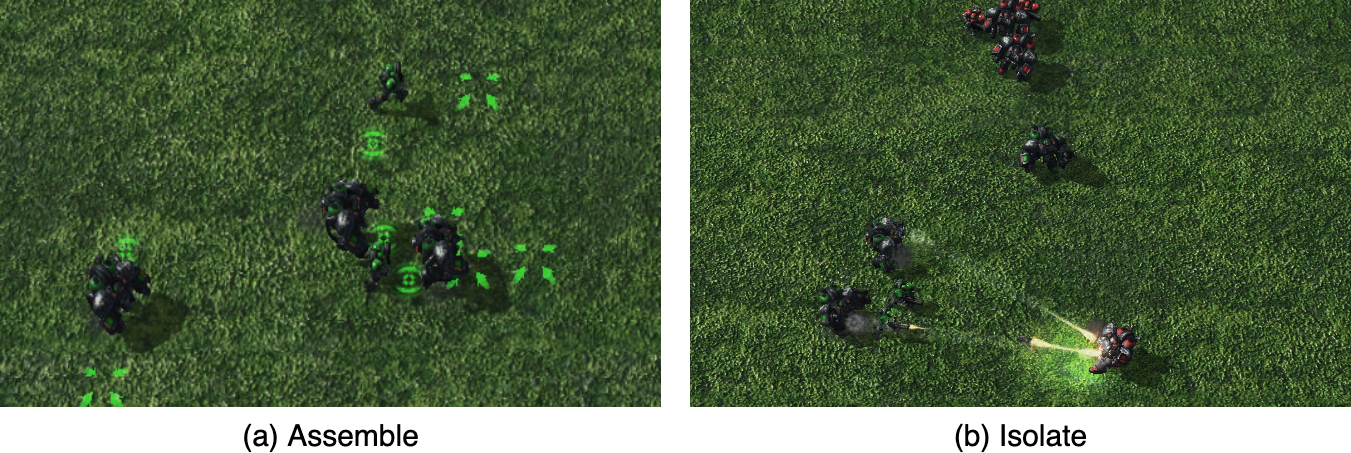
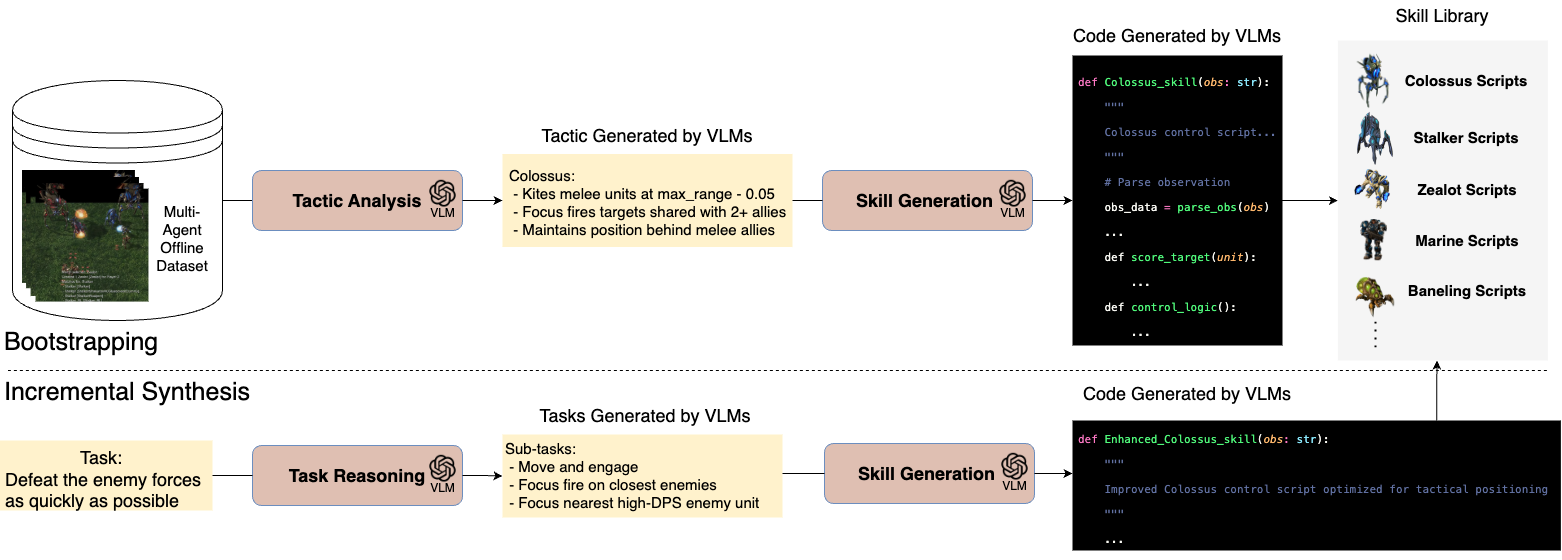
VLMs perform bootstrapping by analyzing offline data for initial tactic analysis and skill generation into a skill library. Incremental synthesis uses task reasoning and self-reflection to dynamically generate or enhance code-based skills.
A New Paradigm for Multi-Agent Systems
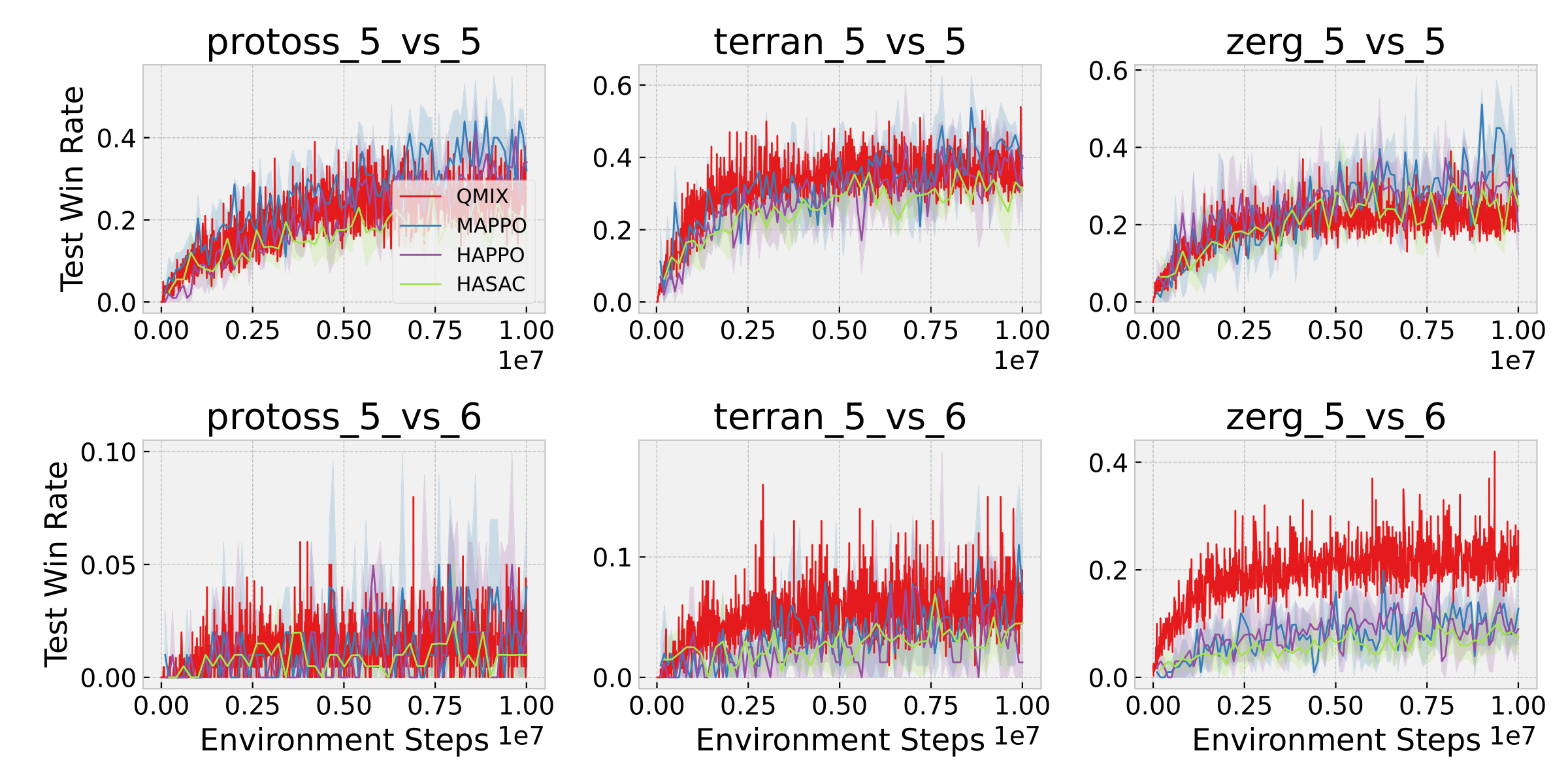
We present COMPASS, a novel multi-agent architecture that integrates vision-language models (VLMs) with a dynamic skill library and structured communication for decentralized closed-loop decision-making.
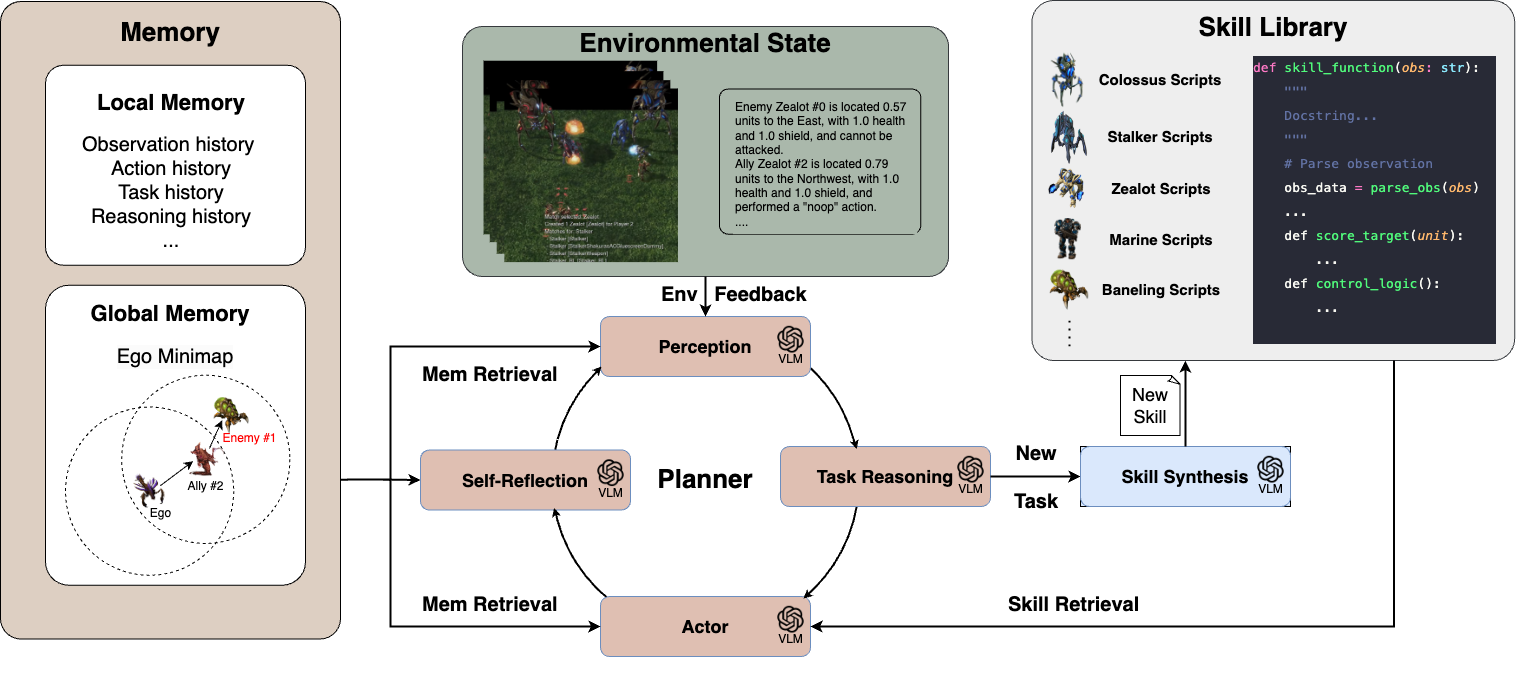
Overview of the COMPASS architecture. A novel framework that advances cooperative multi-agent decision-making through three synergistic components: (1) A VLM-based closed-loop planner that enables decentralized control by continuously processing multi-modal feedback and adapting strategies; (2) A dynamic skill synthesis mechanism that combines demonstration bootstrapping with incremental skill generation; and (3) A structured communication protocol that facilitates efficient information sharing through entity-based multi-hop propagation.
VLM-Based Planning
Decentralized control through continuous processing of multi-modal feedback, addressing non-Markovian challenges in multi-agent systems.
Dynamic Skill Synthesis
Combines demonstration bootstrapping with incremental skill generation, improving sample efficiency and interpretability.
Structured Communication
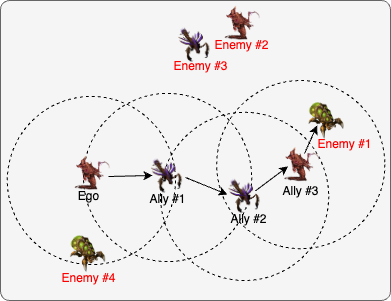
Entity-based multi-hop propagation enables efficient information sharing under partial observability.
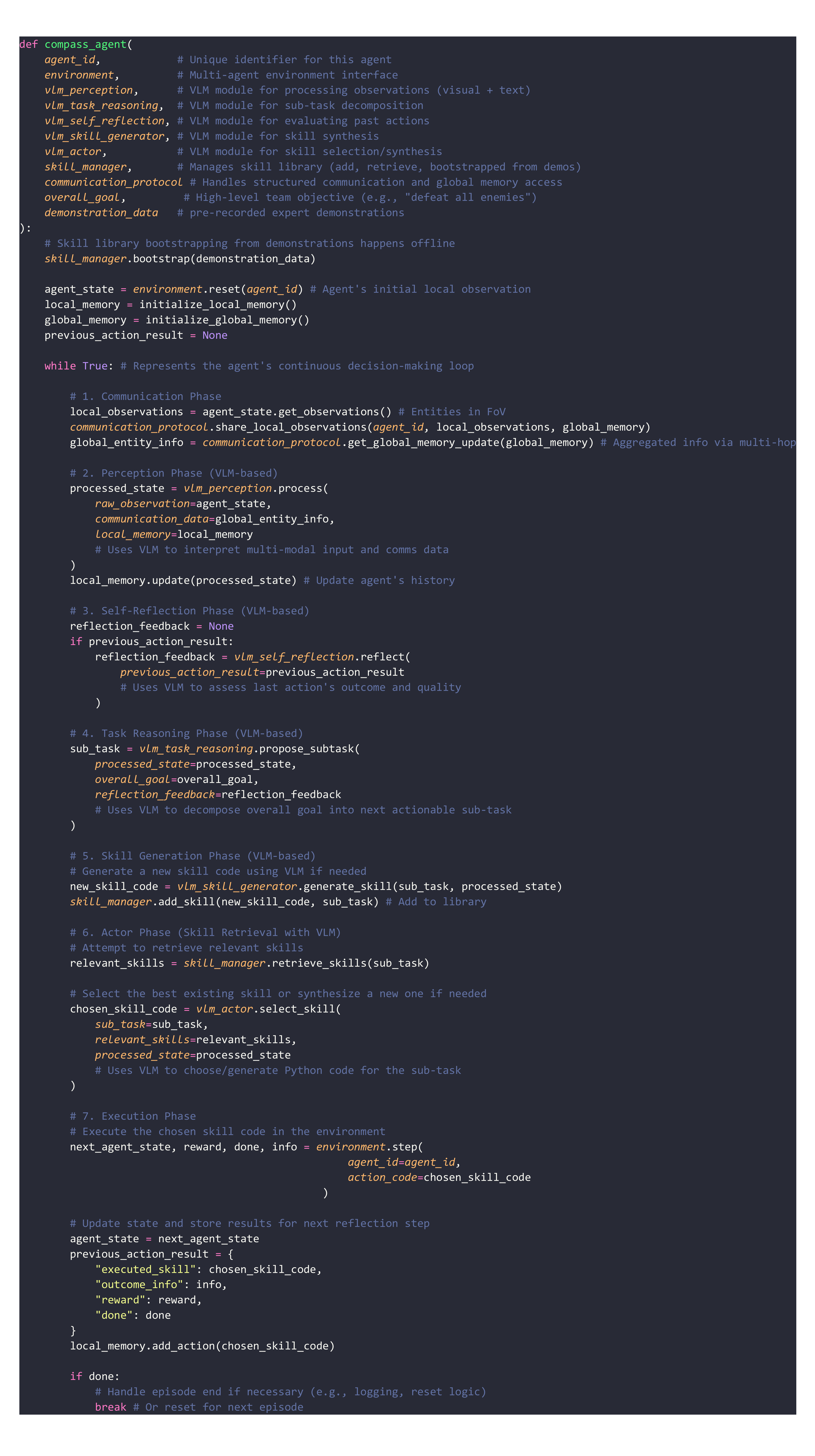
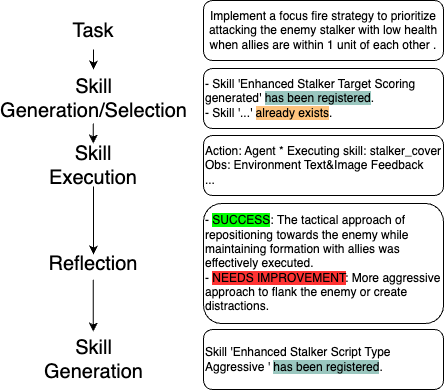
Algorithm: COMPASS Agent Decision Loop. The pseudo-code illustrates the complete decision-making pipeline of a COMPASS agent, including: (1) Communication phase for sharing local observations, (2) Perception phase using VLM to interpret multi-modal input, (3) Self-reflection phase to assess previous actions, (4) Task reasoning phase for goal decomposition, (5) Skill generation and retrieval phases, and (6) Execution phase for environment interaction.